24/7 Carbon-Free Energy: United States
Incentivize a diverse clean energy technology mix
Overview
Companies commonly use energy attribute certificates, known as EACs, to meet their renewable energy goals. Over one-third of companies that have signed up to the RE100 initiative purchase clean power in this way. EACs are awarded to generators per megawatt-hour of renewable electricity produced, and are often used to supplement 100% renewable energy goals when contracted renewable energy does not meet demand.
However, accounting for 100% renewable energy through EAC purchases is usually done on a monthly or annual basis, and often does not match the exact amount of renewable electricity physically consumed. Since renewable energy sources like wind and solar produce energy intermittently, other sources of electricity generation, including fossil fuels, compensate during hours when renewable energy output is low. Matching generation and consumption on an annual, monthly, or even daily basis thus ignores the real-time imbalance between renewable energy supply and demand.
A new accounting method, time-based energy attribute certificates (T-EACs), gives buyers the ability to match their consumption with renewable electricity supply on an hourly or sub-hourly basis. These certificates can help companies and organizations with round-the-clock clean energy procurement targets match every hour of demand with clean power supply.
Impact
The goal of 24/7 carbon-free energy has become the gold standard for clean power commitments among corporations. What 24/7 carbon-free energy means in practice is that a company must fully offset its electricity consumption on an hourly basis, not an annual one. In October 2018, Google became the first company to employ a 24/7 carbon-free energy strategy and since then, companies like Microsoft and Iron Mountain have adopted similar plans. EnergyTag, a UK-based non-profit, is working to reform and standardize T-EACs so that companies hoping to adopt 24/7 carbon-free energy can more accurately track and verify their real clean energy requirements.
Illustration of monthly electricity supply and consumption of a 100% renewable company
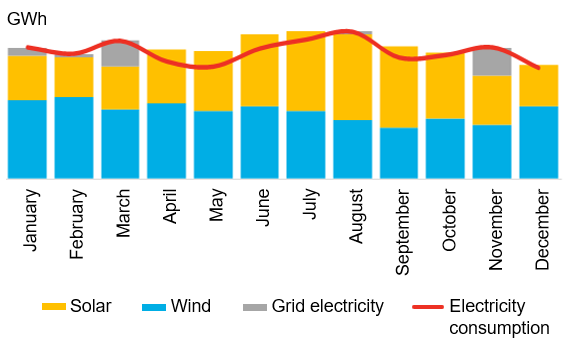 * Source: BloombergNEF. Note: Annual electricity consumption is based on annual solar and annual wind generation. Volumes are not based on real values.
* Source: BloombergNEF. Note: Annual electricity consumption is based on annual solar and annual wind generation. Volumes are not based on real values.
Illustration of monthly electricity and consumption of a 24/7 carbon-free company
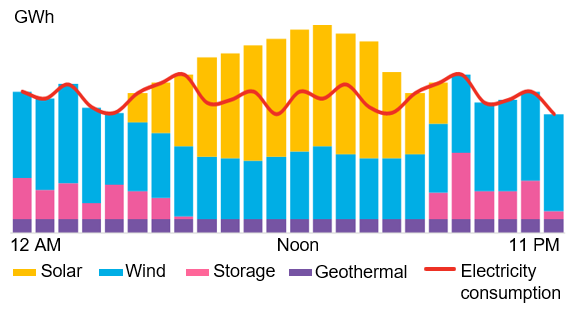 * Source: BloombergNEF. Note: Each bar refers to an hour of the day. Volumes are not based on real values.
* Source: BloombergNEF. Note: Each bar refers to an hour of the day. Volumes are not based on real values.
Google is a supporter of the EnergyTag initiative and has promoted the use of T-EACs as an industry standard. The company has initiated four pilot projects around the world as of June 2023 in partnership with stakeholders. As momentum grows, more registries are developing solutions to offer T-EACs, including M-RETS, PJM GATS, and NAR in the US, and Certigy in Europe. More policymakers are setting hourly targets too, such as the US federal government’s goal to run on at least 50% 24/7 carbon-free energy by 2030.
Opportunity
The expansion and standardization of T-EACs would allow more companies to commit to 24/7 carbon-free energy and improve the EAC market by enhancing transparency, efficiency and accuracy. However, T-EACs cannot be scaled without coordinated action and widespread adoption among policymakers, registries and companies, in order to increase the availability of hourly issuance and trading platforms for granular standardized certificates.
Read next
Related actions
Incentivize a diverse clean energy technology mix
- Power and Grids
- Companies